Future Jobs: A Comprehensive Analysis of The Potential Impact of AIGC
“How will AI shape the future jobs?” This question lies at the heart of the World Economic Forum’s latest white paper, Jobs of Tomorrow: Large Language Models and Jobs, delves into evaluating how artificial intelligence (AI) can automate or enhance various jobs. This groundbreaking report provides a comprehensive analysis of the potential impacts of AI-generated content (AIGC) on the workforce.
-
-
The white paper primarily examines how artificial intelligence can be used to automate or enhance various jobs.
-
-
-
Routine tasks and repetitive jobs are most likely to be automated and thus disrupted by artificial intelligence, while professions that involve critical thinking and complex problem-solving can be enhanced by AI.
-
-
-
It is crucial to ensure that workers have the necessary skills to adapt to the evolving nature of work, and the white paper offers four recommendations on this matter.
-
Automation vs. Enhancement
Jobs Susceptible to Automation
Routine tasks and repetitive jobs are most likely to be automated and thus disrupted by AI. Professions that heavily involve day-to-day routine and repetitive language tasks, such as credit authorizers, cashiers, and clerks, face the highest risk of automation. The white paper highlights that up to 81% of tasks in these roles could be automated by AI.
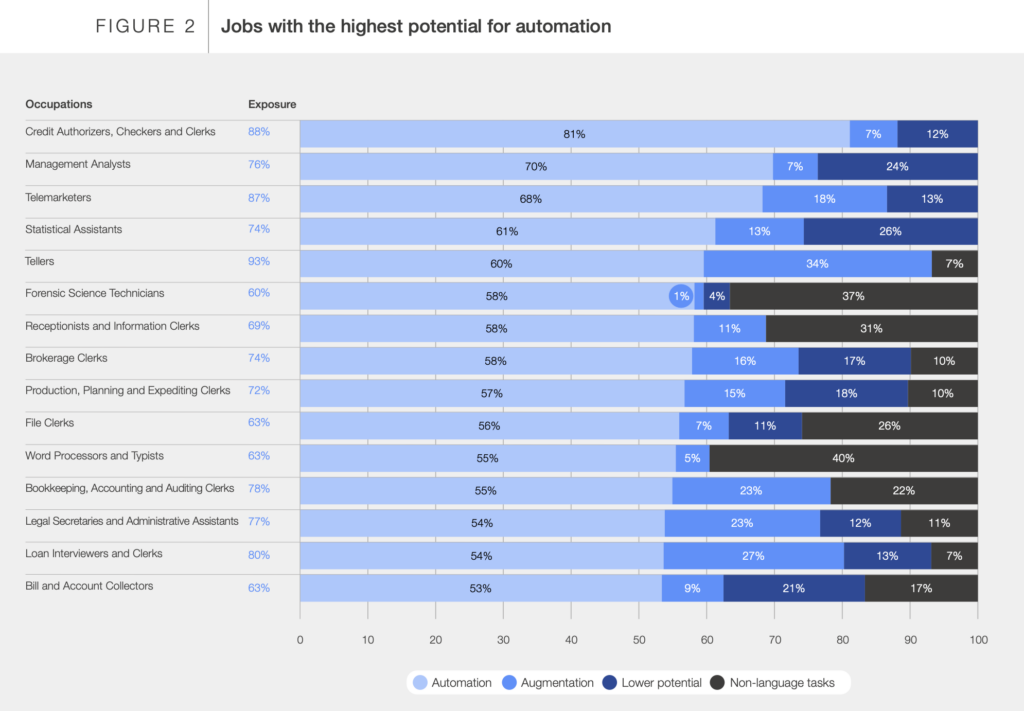
Even other roles, like telemarketers (68%), statistical assistants (61%), and bank tellers (60%), show significant potential for automation, though not as high as clerks and cashiers. The white paper states, “Since 62% of all work tasks involve language, large language models (LLMs) could significantly impact various professions. Their rich functionality and ease of use suggest that many job tasks and closely related professions could be affected by LLMs.”
Jobs Likely to Be Enhanced
Conversely, jobs requiring critical thinking and complex problem-solving skills can be enhanced by AI rather than replaced. AI can boost productivity by saving workers time, especially in tasks involving mathematical and scientific analysis. For instance, insurance underwriters could see 100% of their tasks enhanced by AI, while bioengineers and biomedical engineers could benefit in 84% of their tasks. AI can assist mathematicians with up to 80% of their tasks, and editors could see a 72% enhancement in their work.
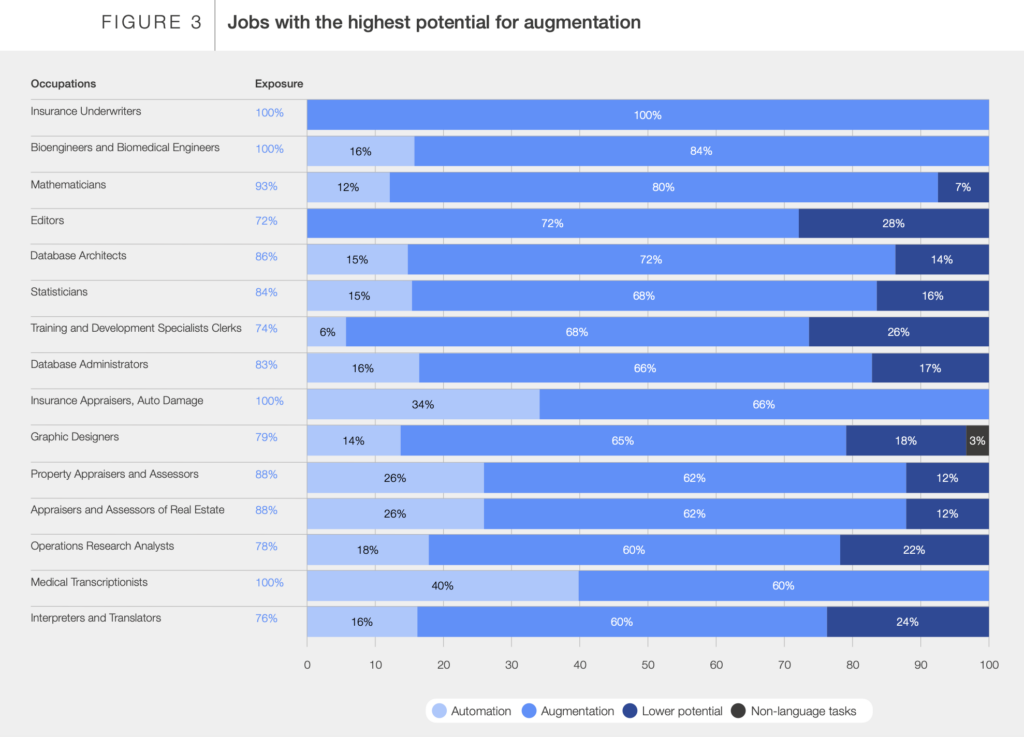
The white paper notes, “Tasks most likely to be enhanced are those requiring more abstract reasoning skills, particularly those involving human interaction.” This explains why roles like journalists, travel agents, and training specialists could see significant benefits from AI enhancement.
Jobs Less Affected by AI
Jobs that require frequent interpersonal interactions are less likely to be disrupted by LLMs. Healthcare workers, teachers, social workers, career counselors, and human resources managers fall into this category. For example, only 16.1% of HR managers’ tasks are susceptible to automation, with 22.2% potentially benefiting from AI enhancement. In comparison, software developers could see 28.7% of their tasks automated and 43.2% enhanced by AI.
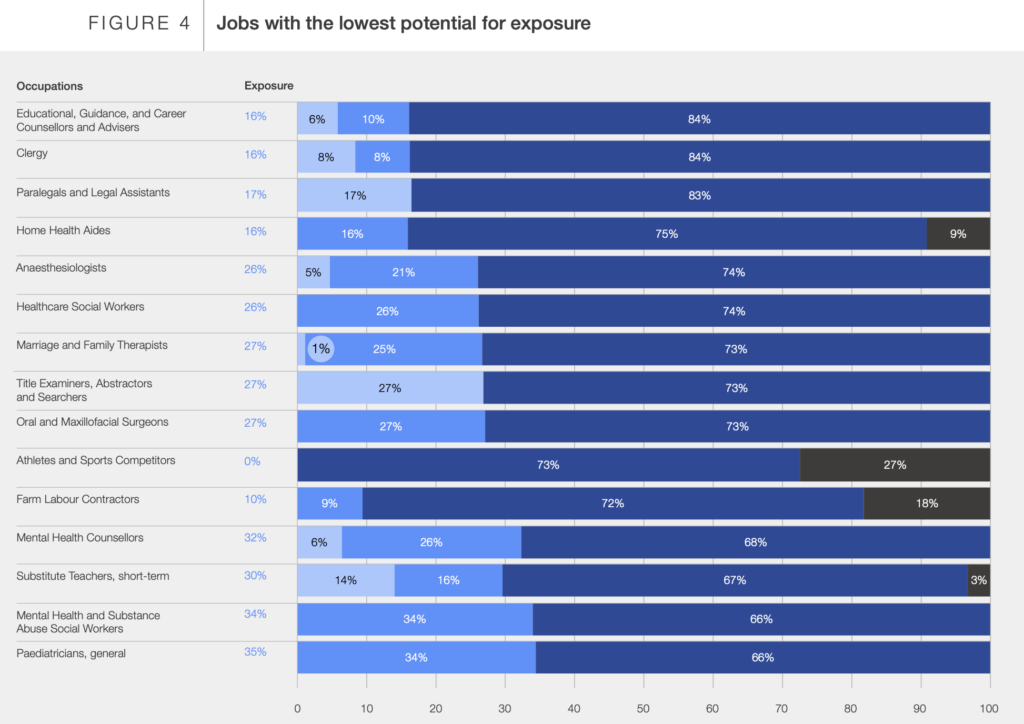
Physical labor-related jobs, such as manual laborers, hairdressers, agricultural workers, and road maintenance workers, also show lower automation potential.
Industries Most Affected by AI
The financial services industry is identified as the most affected by AI automation and enhancement. Other industries significantly impacted include information technology, digital communication, media, entertainment, and sports.
However, the white paper emphasizes that this impact does not necessarily mean job losses. It argues, “Industries with high potential for using LLMs also have significant potential for productivity enhancement. The introduction of new technology will change the nature of the labor market but not necessarily result in job loss.”
Recommendations for Addressing AI’s Impact
To ensure workers can adapt to the changing nature of work, the white paper offers four key recommendations:
-
- Build a Resilient Workforce: Provide training programs that equip employees with AI literacy and interpersonal skills such as creativity, empathy, and strategic thinking.
-
- Strengthen Government and Corporate Cooperation: Foster collaboration to anticipate changes, create new systems and processes, and assist workers in transitioning to new roles.
-
- Revise Labor Laws: Update labor laws to reflect the evolving nature of work, including redesigning social safety nets to address income inequality potentially exacerbated by AI.
-
- Invest in Education Systems: Ensure education curricula are aligned with the AI era and promote lifelong learning. Make education accessible and affordable to prevent anyone from being left behind.
AI’s influence extends beyond automation and productivity enhancement. It also accelerates changes within employers themselves. The white paper suggests that these changes are generally positive, viewing them as “a way to expand human potential and enhance economic resilience.” Achieving this requires collaboration among business leaders, educators, and policymakers.
For employers, the impacts of AI and the green transition bring significant shifts in talent and employment landscapes. The World Economic Forum’s “Good Work Alliance” is assisting employers in preparing for these changes by developing guiding frameworks that outline overall goals, specific metrics, and quantifiable targets for attracting and retaining the necessary talent.
For employees, the World Economic Forum’s “Reskilling Revolution” aims to provide better education, skills, and economic opportunities to 1 billion people, helping them prepare for the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
In conclusion, while AI is poised to transform the nature of work significantly, its impact can be managed and leveraged to enhance human potential. The proactive steps outlined in the white paper are critical to ensuring a smooth transition into this new era.hhhhh
